WORKING OF SOLAR SYSTEM
Sunlight is made up of photons. Photons contain various amounts of energy, corresponding to the different
wavelengths of the solar spectrum. So, when Photons strike a Solar PV Cell (a semiconductor), they get
reflected or absorbed or pass through. The absorbed photon’s energy when knock an electron in an atom of PV
cell it frees the electron from atom, thus generating a flow of electricity. This way Solar PV Module convert
sun’s energy into direct current (DC). But As most homes and business run on alternating current, So, the DC
current is then passed through an Inverter to convert it into usable AC current. At that point, you either
use the electricity in your house or send it back to the electric grid.
NOTE: Solar systems should be sized to not exceed the load demand during the day. If solar power being generated exceeds consumption at that point in time, wastage can be avoided by storing the excess power.
- Capacity of the solar system depends on the amount of electricity required per day by the consumer.
- The size of the solar system also depends on the shadow free space available on the rooftop.
- 1 KW installed solar system can generate 4-4.5 kW-hr of power during a day.
- Shadow free area required by 1 KW system is approx. 100 sq.ft. or 10 sq.mtr.
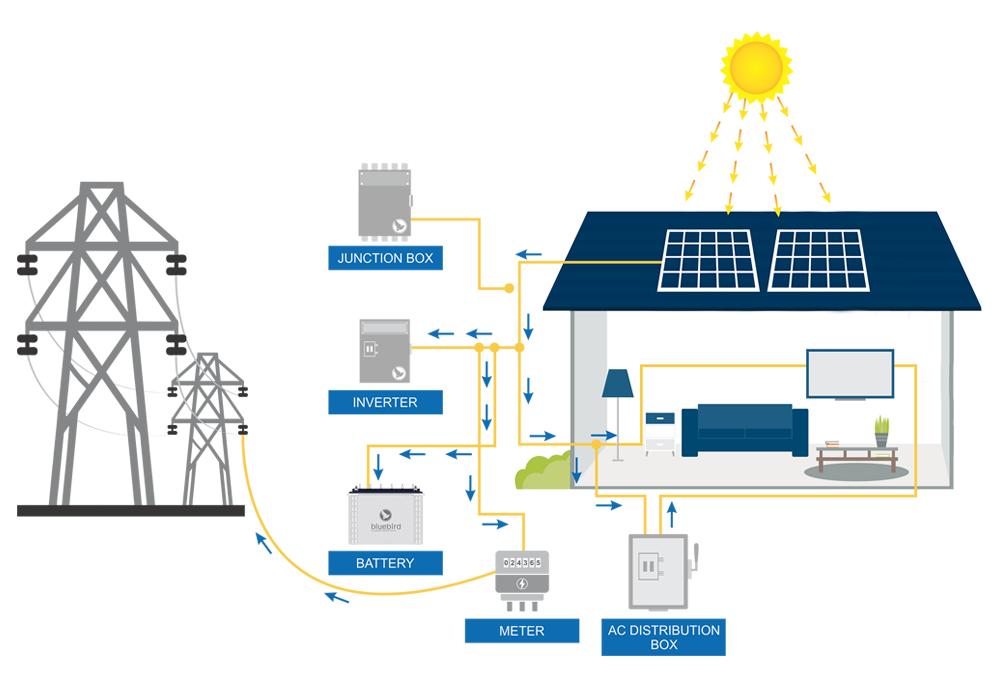
- PV ARRAY consists of SOLAR MODULES interconnected with each other.
- Solar Panels are held on MODULE MOUNTING STRUCTURES, made of galvanized iron, mild steel or aluminium.
- The solar panels should be inclined at a horizontal tilt facing either south or east – west.
- JUNCTION BOX (or ARRAY COMBINER BOX) connects the modules in series or parallel to achieve optimum voltage required by inverter.
- SOLAR INVERTER converts the DC from solar panels to AC, to make it usable for home appliances. It is also connected to the BATTERIES and responsible for managing the charging and discharging of batteries.
- The output of the inverter is connected to a DISTRIBUTION BOX (ACDB), which consists of meter, fuse, MCB and load connections.
- CABLES connect solar modules, junction box, inverters and distribution boxes.
Case-1
PV energy more than connected load
EB GRID not Required
Battery not fully charged
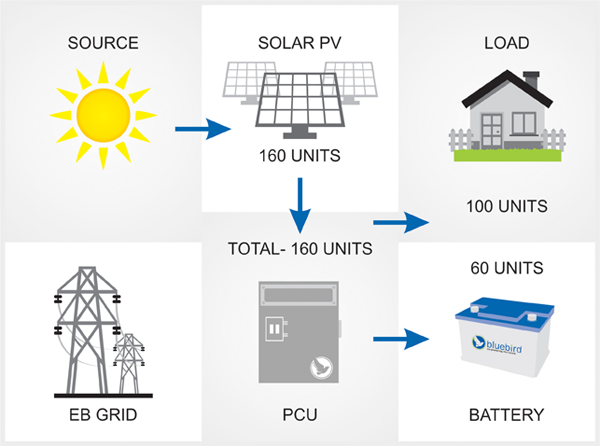
When energy produced by the solar system is greater than the connected load, the excess energy is used to charge the batteries. The grid is not used in this case.
Case-2
PV energy less than connected load
EB GRID power available
Battery not fully charged
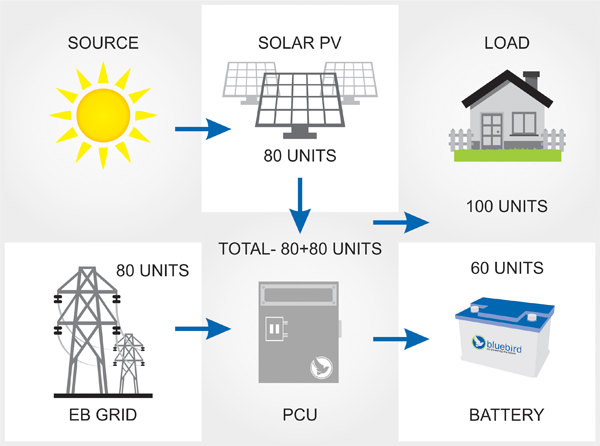
When energy produced by the solar system is less than the connected load, both grid & solar system power the load and charge the batteries.
Case-3
PV energy less than connected load
EB GRID power available
Battery fully charged

When energy produced by the solar system is less than the connected load and the batteries are fully charged, both grid & solar system power the load, keeping solar as a priority.
Case-4 (Daytime Powercut)
PV energy less than connected load
EB GRID power not available
Battery charged
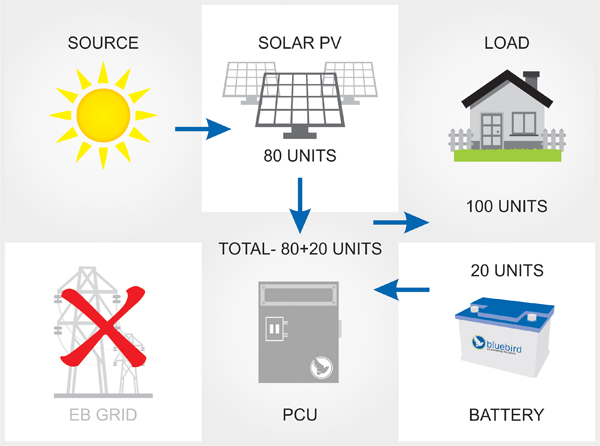
During a day time power cut, batteries & solar system are used to power the load, keeping solar system as a priority.
Case-5 (Night time Powercut)
PV energy not available. EB GRID power not available.Battery charged and works purely as an inverter. Supply directly proportionate to battery charge.
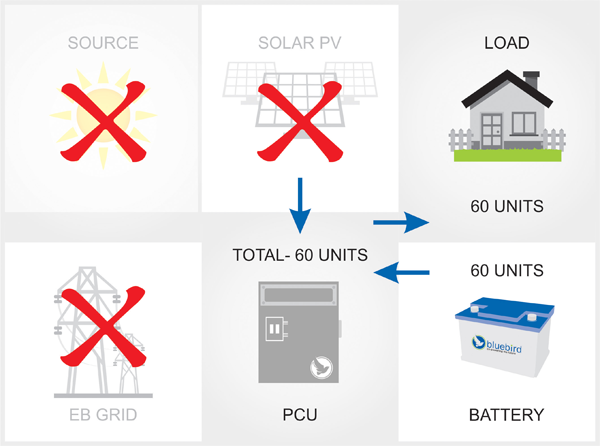
During a night time power cut, batteries are the only source to power the load.